Definition of "Heart block"
Last modified: 1 day
Heart block are conditions that causes a fault within the heart's natural pacemaker, due to some kind of obstruction/block in the electrical condition system of the heart.
Sx
- Asymptomatic, in some cases, despite the severe sounding name
- Occasional missed beats, in some cases, which can cause lightheadedness, syncope/fainting, and palpitations
- May require an artificial pacemaker to be implanted, depending upon exactly where in the heart conduction is being impaired and how significantly it is affected
Pathophysiology
- The heart uses electrical signals to maintain and initiate the regular heart beat in a living person, so incorrect conduction can cause mild/serious Sx, depending upon the location of the blockage, and how severely conductino is being blocked
- Conduction is normally initiated by the SA node (sinoatrial, or sinus node), and then travels to the AV node (atrioventricular node), which also contains a secondary pacemaker, that acts as a backup for the SA Nodes, then to the bundle of His, and then via the bundle branches, to the point of the apex of the fascicular branches
Classification
Blockages are classified based on where the blockages occur, including:
- SA block, at the SA node, the electrical impulse is delayed or blocked, on the way to the atria, thus delaying atrial depolarization. It includes:
- 1st degree SA block
- 2nd degree SA block, including:
- 2nd degree type 1 (Wenckebach block)
- 2nd degree type 2 (Sinus exit block)
- 3rd degree SA block
- AV block, at the AV node, which occurs in the AV node and delays ventricular depolarization. It is divided into:
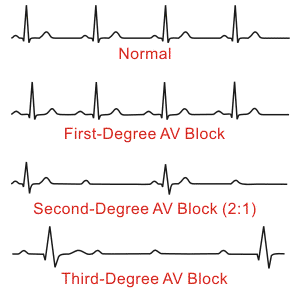
- 1st degree AV block, where the PR-interval is prolonged (>5 small squares). It is caused by a conduction delay through the AV nodes, but electrical signal eventually able to reach ventricles. Often trained athletes can have it. it rarely causes any problems
- 2nd degree AV block, divided into:
- Type 1 (aka Wenckebach block, Mobitz 1), which has a progressive lengthening PR interval, followed by a dropped P wave and QRS complex, due to failure of conduction of the atrial beat. It is caused by a conduction block of some, but not all atrial beats getting through to the ventricles
- Type 2 (aka Mobitz 2), where p-waves are usually at a ratio of 2:1 or 3:1, i.e. quite a few more dropped QRS. It is due to electrical excitation intermittently failing to pass through the AV node or bundle of His
- 3rd degree AV block (aka complete heart block), where atrial contractions are normal, but no electrical conduction is conveyed to the ventricles. Rather, the ventricles generate its own signal from somewhere within the ventricle. Rate is slow, QRS is prolonged, P wave is unrelated and faster than QRS
Source: My Kentucky Heart
- Intra-Hisian block, at the bundle of His
- Infra-Hisian block, below the bundle of His, which may occur:
- Bundle branch block, at the L or R bundle branches
- Fascicular block (aka hemiblock), the fascicles of the left bundle branch
Tx
- Inserting an artificial pacemaker, in severe cases where the heart's ability to control and trigger heartbeats are completely ineffective/unreliable. It is a medical device that provides correct electrical impulses to trigger heat beats, compensating for the natural pacemaker's unreliability
Prognosis
- Heart block frequently is asymptomatic, or has only mild/occasional effects, and is not life threatening in the vast majority of cases
- It is treatable in the more serious cases
- The blocks tend to have more serious potential the closer they are to the end of the electrical path (i.e. the muscles of the heart regulated by the heartbeat), and less serious effects the closer they are to the start (at the SA node). This is because the potential disruption becomes greater as more of the path is blocked, from it's end point. Thus, most of the important heart blocks are the AV nodal blocks and infra-Hisian blocks. In contrast, SA blocks are of lesser clinical significance, since in a SA block, the AV node contains a secondary pacemaker which would maintain a HR of 40-60bpm, sufficient for consciousness, and much of daily life in the majority of Pt's
See also
- Arrhythmia (category)
- Coronary heart disease (damages the heart's blood VESSELS, and can cause angina/chest pain, or MI/heart attack)
- ECG
Synonyms:
1st degree AV block
1st degree block
1st degree heart block
2nd degree block
2nd degree heart block
3rd degree block
3rd degree heart block
Atrioventricular block
AV block
AV node block
Complete heart block
Conduction abnormalities
Conduction abnormality
Conduction block
Conduction delay
Fascicular block
Hemiblock
Incomplete heart block
Infra Hisian block
Intra Hisian block
Mobitz 1
Mobitz 2
SA block
SA node block
Wenckebach
Wenckebach block
Find a practitioner
Practitioner count: 0
Sponsor a disease. And see how your proceeds help.
$1
Express interest
$10
Write text
$40
Write FAQ
$100
Snap photos
$400
Record audio
$1k
Produce video
$4k
Interview experts